The planets average surface temperature has risen about 212 degrees Fahrenheit 118 degrees Celsius since the late 19th century a change driven largely by increased carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere and other human activities. Carbon dioxide for example absorbs energy at a variety of wavelengths between 2000 and 15000 nanometers a range that overlaps with that of infrared energy.
The Science Climate Institute

Properties American Chemical Society
How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming
The Earth then radiates its own heat back up in the form of infrared rays.
Why does co2 absorb infrared radiation. Other forms of electromagnetic radiation in clude radio waves microwaves infrared ra diation ultraviolet rays X-rays and gamma rays. An effective absorber of infrared radiation has a broader absorption profile which means that it can absorb a wider spectrum of wavelengths. On Earth human activities are changing the natural greenhouse.
That is over a 20-year period it traps 84 times more heat per mass unit than carbon dioxide CO 2 and 105. The atmosphere deflects some of this radiation while the rest hits the planetary surface and warms the land and oceans. There the radiation is trapped by glass window panes which are optically opaque in the infrared region of the spectrum.
4 Most of the warming occurred in the past 40 years with the seven most recent years being the warmest. Explore the atmosphere during the ice age and today. Of the remaining 1 percent the main molecules that can absorb infrared radiation are CO2 and water vapor because their atoms are able to vibrate in just the right way to absorb the energy that the Earth gives off.
The majority of Earths atmosphere N2 and O2 are not good greenhouse gas. The goal of our measurements is to quantify how much CO 2 has been added to or removed from the atmosphere. The concentration of a gas is defined formally as the number of molecules per cubic meter.
Most objects radiate infrared energy which we feel as heat. Over the last century the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide CO 2This happens because the coal or oil burning process combines carbon with oxygen in the air to make CO 2To a lesser extent the clearing of land for agriculture industry and other human. The sensors detect the reduction in transmitted IR light which proportionate to gas concentration.
The next most significant greenhouse gas is surface or low-level ozone O 3Surface O 3 is a result of air pollution. However since low levels of CO2 do not absorb much light a long tube is needed before the effect can be measured. How do greenhouse gases affect the climate.
Harries 2001 does look at the full infrared spectrum except for wavelengths less than 700nm which happens to be where a large portion of the CO2 absorption occurs. Energy flows between space the atmosphere and Earths surface with greenhouse gases in the atmosphere capturing a substantial portion of the heat reflected from the earths surface. The heated surface emits infrared light.
Zoom in and see how light interacts with molecules. As a result the amount of light radiation that is absorbed by the CO2 molecules is proportional to the amount of carbon dioxide in the gas sample. Gasses like CO2 do not only absorb infrared radiation but they also re-emit the same radiation this time in whathever direction partly back to the earth.
The observed changes in the spectrum from 1970 to 2006 are consistent with theoretical expectations. From infrared spectroscopy we know some gases absorb infrared energy in the infrared area. Then compare to the effect of glass panes.
Water vapor and carbon dioxide can absorb radiation wavelengths in the range of 4 μm to 80 μm except those between 8 μm and 12 μm. The outer edges of the shoulders of the absorption peaks are said to be unsaturated because they dont absorb all radiation available to them. Do all atmospheric gases contribute to the greenhouse effect.
It must be distinguished from naturally occurring stratospheric O 3 which has a very different role in the planetary radiation balanceThe primary natural source of surface O 3 is the subsidence of stratospheric O 3 from the. CO 2 molecules absorb infrared light at a few wavelengths but the most important absorption is light of about 15 microns says Kroll. Incoming light from the sun tends to have much shorter wavelengths than this so CO 2 doesnt stop this sunlight from warming the Earth in the first place.
All of these known collectively as the electromagnetic spectrum are fundamentally similar in that they move at 186000 miles per second the speed of light. Since the infrared radiation does not pass through the. Tekhasski you sure can pile on the jargon but the basic argument is not affected by what you or GMB are saying.
Why do we express the abundance of CO 2 as a mole fraction in dry air. This is also the process that warms the plants in a greenhouse the glass roof does not absorb the visible light coming in from the sun but the infrared radiation. With CO2 and other greenhouse gases its different.
Change the greenhouse gas concentration and see how the temperature changes. Greenhouse gases allow sunlight to pass through the atmosphere but then absorb and reflect the infrared radiation heat the planet emits Quantitative analysis. As the atmosphere warms more infrared radiation is radiated to space.
This image is the distance infrared radiation travels at the present concentration of CO2 in the air. The 20-year global warming potential of methane is 84. The years 2016 and 2020 are tied for the warmest.
Atmospheric methane concentrations are of interest because it is one of the most potent greenhouse gases in Earths atmosphere. Non-Dispersive Infrared SensorsNDIR When infrared IR radiation interacts with gas molecules the gas molecules absorb the light at a particular wavelength causing vibration of the gas molecules. Atmospheric methane is rising.
What happens when you add clouds. CO2 levels affect ragweed pollen production with plants that grow at higher CO2 levels producing more pollen CO2 levels affect the concentration of allergens the proteins that actually trigger allergic reactions found in ragweed pollen with plants that grow at higher CO2 levels characterized by pollen with higher concentrations of allergensNext the researchers designed experiments to. Some of the wavelengths of solar radiation traveling through the atmosphere may be lost because they are absorbed by various gases.
About 99 percent of the atmosphere is made of oxygen and nitrogen which cannot absorb the infrared radiation the Earth emits. The remaining solar radiation is the longest wavelength infrared. While oxygen O2 is the second most abundant gas in our atmosphere O2 does not absorb thermal infrared radiation Michael Daley an associate professor of environmental science at Lasell.
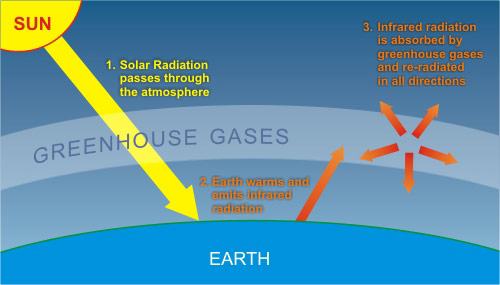
The band of infrared radiation is very close to the absorption band of CO2. But a fraction of the infrared emitted by the Earth is absorbed by these molecules which then reemit it frequently back to the Earth. The Greenhouse Effect on Earth The ground is heated by visible and some infrared light from the Sun.
Atmospheric methane is the methane present in Earths atmosphere. Ozone completely removes UVC most UVB and some UVA from incoming sunlight. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation.
Sunlight comes in with a small amount of long-wavelength infrared so does not get absorbed so much by CO2 methane NO2 etc gets absorbed then tries to head out again as blackbody radiation which is mostly in the long-infrared range and is strongly absorbed by the. That is what provides the extra heating. The unsaturated area is virtually nonexistent.
The effect of infrared re-radiation being absorbed in the atmosphere is called the Greenhouse Effect since it mimics what happens in a real greenhouse. The concentration does not give us that information because it primarily depends on the pressure and temperature and. As CO2 soaks up this infrared energy it vibrates and re-emits the infrared energy back in all directions.
CO2 is one of them as is H2O vapour. The small amount of greenhouse gases H2O CO2 traps absorb and re-emit the infrared radiation increasing the temperature of the atmosphere.

Carbon Dioxide How Can A Little Co2 Molecule Be Such A Big Troublemaker

How Exactly Does Carbon Dioxide Cause Global Warming You Asked
Heat Absorbing Gases

C 5 Ir Absorbance Of Greenhouse Gases Sl Youtube
Greenhouse Gases
Does Co2 Absorb All Infrared Frequencies Near Infrared Far Infrared Etc Or Does It Just Absorb One Frequency Quora

Why Carbon Dioxide Has Such Outsized Influence On Earth S Climate
The Greenhouse Effect
