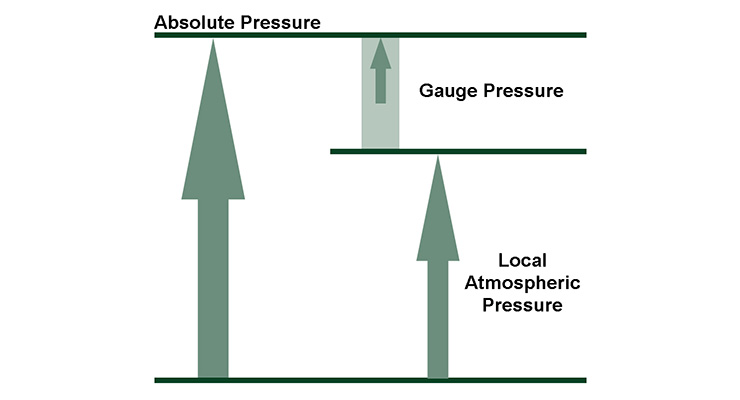
An absolute pressure of zero corresponds to empty space or a complete vacuum. Definition of gauge pressure.
What Does Pressure Really Mean

Atmospheric Pressure And Absolute Pressure Youtube
Absolute Pressure
Atmospheric pressure is a measure of absolute pressure and is due to the weight of the air molecules above a certain height relative to sea level increasing with decreasing altitude and decreasing with increasing altitude.

Absolute atmospheric pressure. Absolute Pressure Defined. The BMP390 is a very small low-power and low-noise 24-bit absolute barometric pressure sensor. At sea level it is around 147 pounds per square inch.
Atmospheric pressure also known as barometric pressure after the barometer is the pressure within the atmosphere of EarthThe standard atmosphere symbol. The a refers to absolute. Because of this the MAP sensor is able to measure the pressure in the intake manifold to gauge vacuum.
If the absolute pressure of a fluid stays constant the gauge pressure of the same fluid will vary as atmospheric pressure changes. Aneroid gauge measures pressure using a bellows-and-spring arrangement connected to the pointer of a calibrated scale. Absolute pressure of a fluid may be more or less than atmospheric depending upon whether the gauge pressure.
Deepest point under sea level of Sognefjorden Norway. When the engine is off the absolute pressure inside the intake equals atmospheric pressure so the MAP will indicate about 147 psi. By adding a pressure of one atmosphere to the.
Pressure is the force per unit area applied to an object in a direction perpendicular to the surface. P0 is the base level pressure at no height 101325 Pa H is the height meters T is the temperature K g is the acceleration due to gravity 98 ms2. Open-tube manometers have U-shaped tubes and one end is always open.
Since the gauge pressure is equal to. Altitude Above Sea Level Absolute Barometer Absolute Atmospheric Pressure. P g p - p a where p a is the local atmospheric pressure.
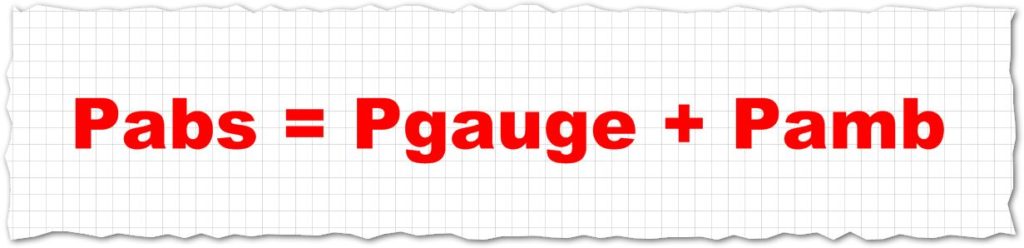
The gauge pressure is calculated by subtracting the atmospheric pressure from the absolute pressure. P abs P atm P gauge. According to the ideal gas law when a gas is compressed into a smaller volume.
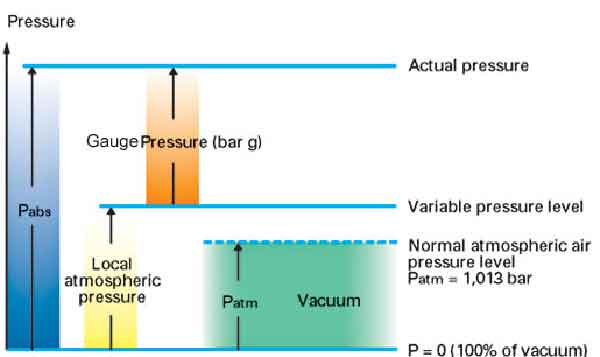
It simply means there is no pressure in excess of the local atmospheric pressure. Vacuum and pressure are inversely proportional when vacuum goes up pressure goes down. A full vacuum has an absolute pressure reading of 0 PSIA and average barometric pressure at sea level is 147 PSIA.
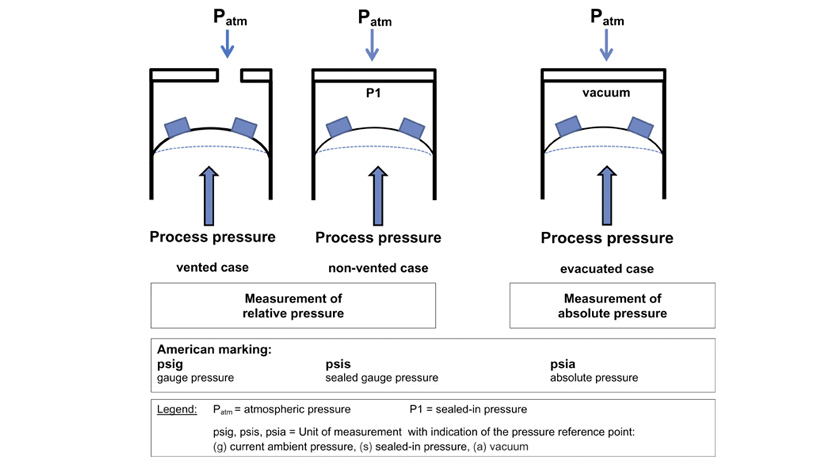
The local atmospheric pressure is 142 psi. It is often used to indicate the depth rating for a water resistant watch but otherwise is rarely used as a unit for measuring pressure. In contrast pressure that is measured against atmospheric pressure also known as barometric pressure is called gauge pressure.
Manifold vacuum is a good indicator of engine load. The vacuum pressure is articulated as Vacuum Pressure Atmospheric Pressure Absolute Pressure. The fluid pressure is also called gauge pressure is the force applied on surface by a fluid liquid or gas without considering the atmospheric pressure.
Atm is a unit of pressure defined as 101325 Pa 101325 hPa. A car tire gauge measures a tire pressure of 320 psi. Where p gauge is the gauge pressure.
Absolute zero pressure can occur only if the molecular momentum is zero and this condition arises when there is a perfect vacuum. P atm is atmospheric pressure. Where P is the atmospheric pressure.
How is gauge pressure calculated. Imagine the 1ft x 1ft area above without the column of liquid above it. 1 standard atmosphere is defined as.
Atm p absolute For example a car tire pumped up to 25 atm 3675 psig above local atmospheric pressure let say 1 atm or 147 psia locally will have an absolute pressure of 25 1 35 atm 3675 147 5145. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. The gauge pressure is defined as the difference between an absolute pressure P abs and the prevailing atmospheric pressure P amb.
The temperature of 293 o K 20 o C is sometimes used. With the engine off manifold pressure and atmospheric barometric pressure are the same. Feet metre inches Hg mm Hg psia kgcm 2 kPa-5000-1524.
What is the absolute pressure of the air in the tire. Standard Atmosphere is mainly used as a reference value for the average atmospheric pressure at sea level. It is denoted with the subscript abs.
In imperial units the Standard Atmospheric Pressure is 14696 psi. At sea level atmospheric pressure is about 147 psi pounds per square inch. Gauge pressure is a pressure measured by an instrument without taking into account the atmospheric pressure around it.
Absolute pressure formula p abs is given by. Absolute pressure is measured relative to a full vacuum. At a perfect vacuum the MAP sensor will read.
The pressure gauge is equal density multiplied by depth and acceleration. For example an ordinary pressure gauge reading of zero does not mean there is no pressure. Gage pressure is indicated by p g and is related to absolute pressure as follows.
The MAP sensor measures the absolute pressure inside the intake manifold of the engine. The Standard Atmospheric Pressure is defined at sea-level at 273 o K 0 o C and is 101325 bar or 101325 Pa absolute. The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth.
101325 mbar which is equivalent to 760 mm Hg 299212 inches Hg or 14696 psi. Instead the 1ft x 1ft area is at sea level and there is a column of gases above it. Absolute pressure and write 22 psia.
P vacuum p absolute. For instance an absolute pressure of 80 kPa may be described as a gauge pressure of 21 kPa ie 21 kPa below an atmospheric pressure of 101 kPa. Gauge pressure is the additional pressure in a.
Absolute pressure is the sum of gauge pressure and atmospheric pressure. The height relative to sea level conversions are derived using the US Standard Atmosphere 1976 barometric formula for geopotential altitude with the following values1-6 at heights from 5000 ft 1524 m below to 100000 ft 30480 m above mean sea level. Gauge pressure means a pressure which is relative to the atmospheric pressure.
Standard atmospheric pressure of 101325 mb at 0 m 226321 mb at 11000 m 547489 mb at 20000 m above mean sea level. It is that pressure of a fluid which is measured with respect to absolute zero pressure as the reference. Atmospheric pressure is typically about 100 kPa at sea level but is variable with altitude and weather.
The digital high-performance sensor is ideally suited for a wide range of altitude tracking applications such as smartphones GPS modules wearables hearables and drones. This reference pressure is the ideal or absolute vacuum. The conversion factor that needs to be used to convert between gauge pressure and absolute pressure is atmospheric pressure.
Absolute pressure of a gas or liquid is the total pressure it exerts including the effect of atmospheric pressure. Atmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted on a solid liquid or gas by the atmosphere. The absolute pressure is defined as a total pressure at a point in the fluid which is equal to the sum of gauge pressure and the atmospheric pressure.
Here we can calculate for Absolute Pressure Gauge Pressure Atmospheric Pressure.
What Is The Difference Between Absolute Gauge And Differential Pressure

What S The Difference Between Gauge And Absolute Pressure

Atmospheric Absolute Gauge Differential Pressure Tameson Com
What Is Pressure And How Is It Referenced Dwyer Instruments Blog

What Is The Difference Between Absolute And Relative Pressure Ambient Weather Help Center
Mechanical Engineering Projects And Interview Question Pascal S Law Pressure According To Pascal S
Fields Of Application For Pressure Sensors 3 Absolute Pressure Sensors Why Is It Necessary To Use Absolute Pressure Sensors Or Pressure Transmitters Wika Blog

Gauge Pressure Absolute Pressure And Pressure Measurement Physics

